PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUONS
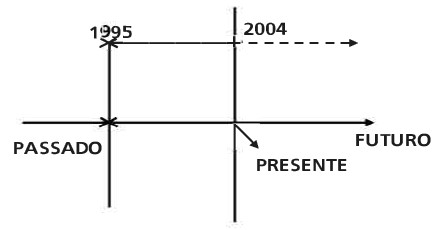
Esse tempo verbal é usado para indicar uma ação progressiva de um certo ponto no passado até o presente, e que tem possibilidades de continuar no futuro. A diferença entre o “Present Perfect Continuous” e o “Present Perfect” é que o primeiro expressa uma possibilidade maior da ação continuar no futuro e também apresenta ênfase na progressão da ação até o presente.
Exemplos:
Pamela has been working at the plant for months.
Judy and I have been studying English since last year.
Formação:
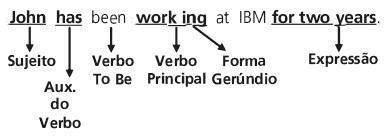
Exemplo:
The scientists have been working on the project since 1995.
CONJUGAÇÃO DO “PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUONS”

PAST PERFECT
Usado para indicar que uma ação (Past Perfect) aconteceu no passado antes de outra ação (Simple Past) no passado.
Exemplos:
Joy had finished the article by 8:00 p.m.
She had never read that author before last night.
I tried to call her, but she had already left.
When I phoned she had just left.
Time Expressions: by, before + (point in time), just, already, never, after, when, before.
Formação:


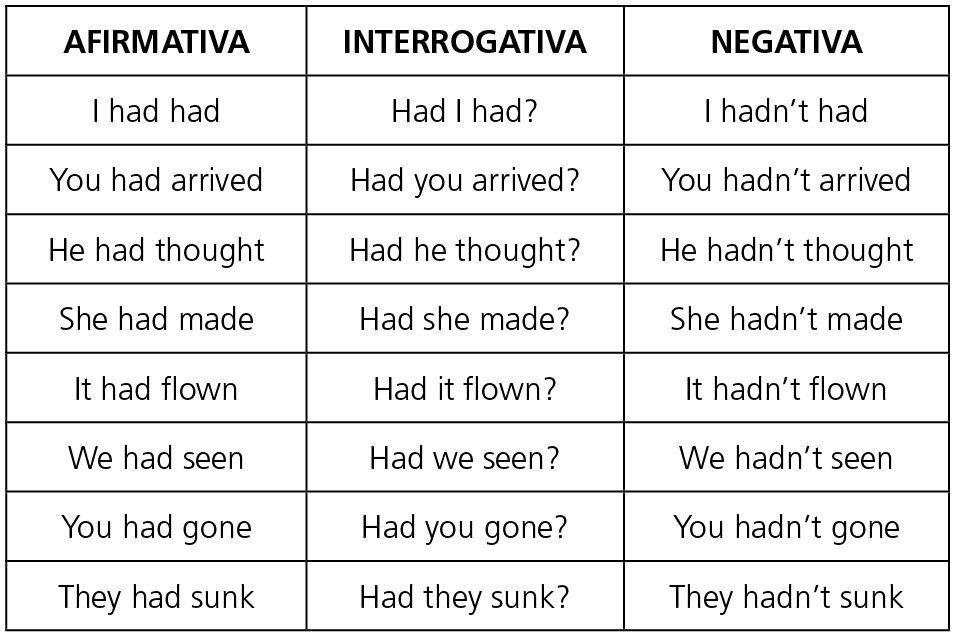
CONJUGAÇÃO DO “PAST PERFECT”
PAST PERFECT CONTINUOUS
Esse tempo verbal descreve uma ação progressiva, iniciando no passado e com término também no passado.
Exemplos:
By midnight, Claudia had already been working for twelve straight hours.
She had been working for fourteen hours when I called her at 2:00 a.m.
After she had been working for sixteen hours, she fell asleep.
She had been sleeping since 4:00 a.m. when she woke up at
8:00 a.m.
Formação:
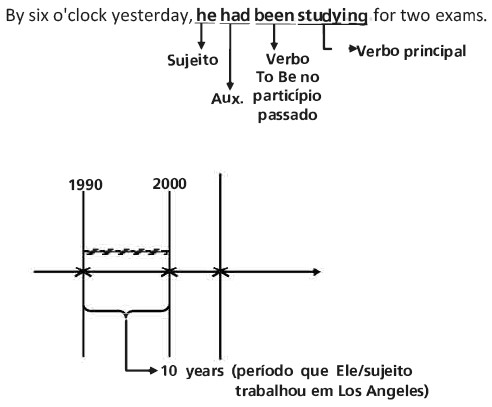
Before his stay in New York, he had been working for ten years in Los Angeles.
CONJUGAÇÃO DO “PAST PERFECT CONTINUOUS”





